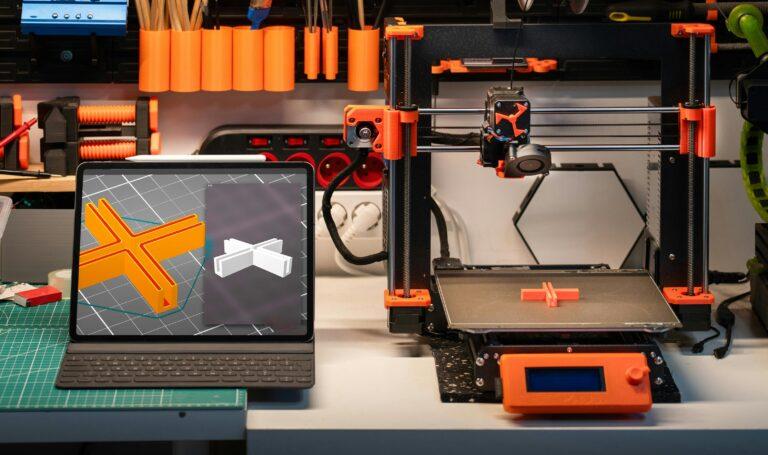
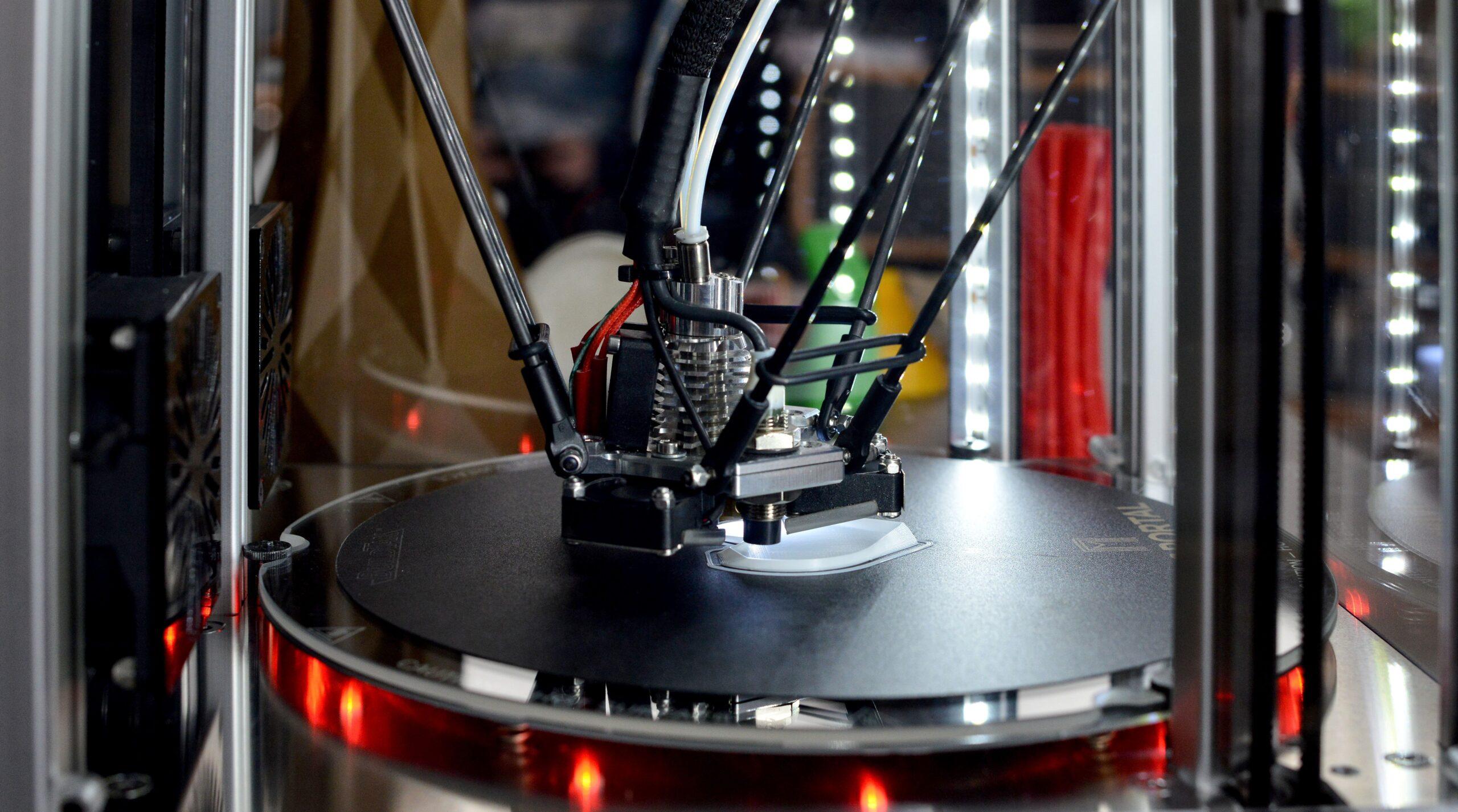
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is an ideal process for the production of prototypes and short series in polyamide. This manufacturing method consists of obtaining physical parts from a design created with 3D software.
It is an excellent process for the manufacture of fully functional parts, since this technology can produce stronger parts than other technologies such as laser synthesizing. These parts are 100% isotopic, i.e. they offer the same resistance in any axis, without forgetting the high precision achieved.
As for how it works, in 3D printing, a 3D digital model is cut into hundreds of thin layers using specific software to export it in G-code format. This format is a language that the 3D printer can read to know exactly when and where to deposit the material.
The layers are printed consecutively in 3D until the desired object is completely printed. Each layer corresponds to the exact 2D shape of a section of the object.
Benefits and applications of 3D printing
This procedure offers a number of advantages, the most important of which is the ability to produce extremely complex designs (which would otherwise be impossible).
On the other hand, another important aspect is speed. Although 3D printing an object can take hours or even days, it is still a much faster production method than other common processes (such as injection molding).
Finally, another key benefit is the wide range of possibilities that additive manufacturing offers in terms of materials.
In terms of applications, 3D printing can be used to manufacture prototypes of a project already designed or in the design phase. Generally, prototyping takes a long time and requires continuous corrections and adjustments that can further increase the manufacturing time. Thanks to 3D printing, parts would cost less and the prototype validation process could be accelerated.
Moreover, it is an ideal process also for printing final parts thanks to the strength and reliability of the 3D parts. In addition to increasingly efficient materials, additive manufacturing is leading the way in the manufacture and development of parts with specific and complex characteristics.
Another application of 3D printing for companies is related to mass production. Thanks to the generation of molds by 3D printing, countless identical productions can be produced.
What is the future of 3D printing?
What was once a novel and innovative technology is now everywhere, solving complex problems in industries at different scales.
Experts say the industry’s biggest breakthroughs will be in technology that facilitates additive manufacturing. This manufacturing method will add versatility and efficiency in many different ways: with the use of different materials, allowing a wider variety of 3D printed structures, increasing its production speed…
3D Printing Techniques: Multi Jet Fusion
There are many techniques currently used for 3D printing, but at Proto&Go! we specialize in Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) printing. This is the latest technology from HP, designed especially for industrial applications.
Using this technology, parts can be manufactured from both rigid and solid materials (such as Polyamide PA12) and robust and flexible materials (such as TPA) to obtain functional engineering components.
In conclusion, we can say that the future of 3D printing for manufacturing parts and prototypes is promising. Companies are investing more and more in implementing this technology and its evolution will not stop here. In the coming years we may see new applications and benefits of 3D printing emerge.
At Proto&Go! we aim to provide you with the best service for the development of your parts through additive manufacturing.
Request your quote now online and receive a quote in less than 24 hours!