Choosing the right material is one of the most decisive factors in any rapid prototyping process. It not only influences the look and feel of the prototype, but also its functionality, cost, and delivery time. Whether you are validating an idea, manufacturing a visual model, or conducting functional tests, understanding the characteristics of the most commonly used materials in prototyping allows you to make better decisions from the outset of development.
In this basic guide, we review the main materials available in technologies such as 3D printing, CNC machining, and silicone molding, their typical applications, and how to choose the most suitable one for each phase of the project.
What is the prototype for, and what materials do you need?
Before choosing a material, it is essential to be clear about the purpose of the prototype. Is it a visual piece for a presentation? A functional model to validate fittings? A component that must withstand temperature or mechanical stress? The answer to these questions will determine whether you need rigid or flexible materials, resistant or lightweight, economical or with premium finishes.
In general, we can distinguish three main types of prototypes:
- Visual prototypes: used to validate form and aesthetics. They require careful finishing, but not necessarily functional properties.
- Functional prototypes: these must behave like the final part. They require technical materials and tighter tolerances.
- Prototypes for testing: used in resistance, stress, or thermal behavior tests. The material must reproduce real conditions as closely as possible.
With this in mind, we review the most common materials in each technology.
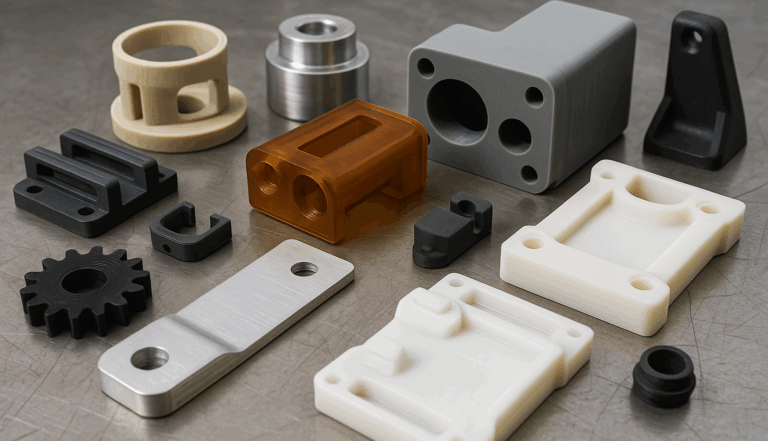
3D printing materials: versatility and speed
3D printing 3D printing is one of the most widely used technologies in rapid prototyping due to its speed, competitive cost, and variety of available materials. Among the most common are:
- PLA: biodegradable, easy to print, and with a good surface finish. Ideal for visual prototypes.
- ABS: more resistant than PLA, suitable for functional parts and assemblies.
- PETG: combines flexibility and strength with good transparency. Useful for parts subject to prolonged use.
- Nylon (PA12): high mechanical strength, good wear resistance. Recommended for technical parts.
- TPU: flexible material, ideal for simulating rubber or gaskets.
- SLA/DLP resins: offer extremely high resolution. Perfect for detailed parts or medical/dental models.
In printing technologies such as SLS or MJF, powdered polyamides are used to manufacture complex geometries without supports and with greater durability.
Materials for CNC machining: precision and robustness
When greater strength or dimensional tolerance is required, CNC machining is the ideal choice. Some common materials used in this process:
- Aluminum (6082, 7075): lightweight, strong, and easily machinable. Ideal for structural parts.
- Stainless steel: offers high hardness and chemical resistance. Widely used in the medical and food industries.
- Brass: excellent for aesthetic prototypes with a gold finish and good machinability.
- POM (Delrin): engineering plastic with high rigidity and low friction. Perfect for moving parts or gears.
- PMMA (methacrylate): translucent, used to simulate glass or transparent plastic parts.
These materials enable the manufacture of prototypes that are almost identical to the final part, useful for testing, assembly, or technical validation.
Silicone mold materials: short runs and flexibility
Silicone molding allows small series of parts to be manufactured in materials similar to injection plastics, based on a master prototype. The most commonly used materials are polyurethane resins that simulate engineering plastics:
- Rigid PU: emulates ABS or PC, useful for casings, covers, technical parts.
- Flexible PU: similar to PP or soft rubbers, suitable for components subject to deformation.
- Transparent PU: alternative to PMMA or PC, for visual parts or lighting fixtures.
This technique is ideal for validating the final product before investing in injection molds.
Proto&Go!: the ideal partner for any type of prototype
At Proto&Go! we understand that every project needs to move forward quickly, reliably, and with technical expertise. That’s why our online rapid prototyping platform allows you to upload your 3D files directly, choose materials and technologies—such as 3D printing, CNC machining, or silicone molding—and receive a quote in less than 24 hours.
Thanks to our specialized team and infrastructure designed for startups, engineers, technology centers, and R&D departments, we deliver functional or visual prototypes in just a few days, tailored to the needs of each phase of development.
Upload your 3D file now and request a quote from our website!